
Best Laser Cutting Service In Bangladesh
Our Laser Cutting service is known for its speed and dependability. Our large fleet of machines and engineering staff provides an in-depth understanding of technology, allowing us to provide the fastest turnaround of any laser cutting service on the market while also producing some of the best cuts in the industry. Our Laser Cutting service will deliver high-quality parts on time and on budget, thanks to industry-leading speeds and efficiency. We work 24 hours a day, seven days a week. That is why our customers continue to return to us. We are extremely proud of our 97 percent customer satisfaction rating.
Why Choose Us For Your Laser Cutting Needs

Professional Service
We respond to urgent laser cutting and engraving requests quickly and professionally. We usually have all of the necessary items in stock and can ship them out within hours.




Quick Turnaround Time
If you have an urgent requirement, let us relieve the stress by providing a quick, cost-effective Laser cutting and engraving solution backed by the highest level of quality and service.




High-end Laser Cut
We can laser cut and engrave a wide variety of materials, including mild steel and acrylic. Our engineers are also equipped with the most up-to-date computer-aided design and electronic cutting technology.
Which Industries Use Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a very adaptable manufacturing method. It’s difficult to provide a comprehensive list, so here are a few examples.


Signs & Display
We’ve got you covered when it comes to signs. To provide you with the most comprehensive laser cut service in Bangladesh, we work in metal, wood, plastic, and even rubber. We are constantly expanding our service offerings to meet your needs.
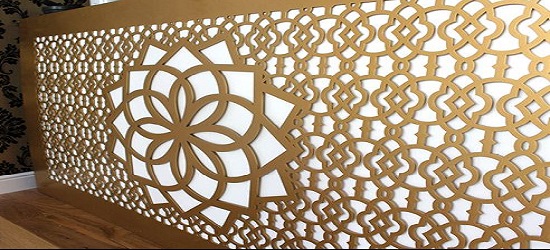

Panels
For both internal and external cladding applications, we can laser-cut panels. Acrylic, anodized aluminum, and heavy gauge mild and stainless steel are among the materials used. For all of your project requirements, we have both standard and bespoke designs.


Brand & Marketing
We’ve already worked with hundreds of companies to develop the right brand image, marketing message, and giveaway. We understand your requirements and have the necessary resources to meet them. Send us a message with your ideas, and you’ll be surprised at how quickly we respond.


Architecture & Interiors
For both interior and exterior applications, we can laser-cut panels. We can laser cut a panel to your exact proportions for your head office and warehouse front premises, dressing rooms, retail hanger room, center court & stage area, snack bar interior, or any other interior/ exterior signage application.


Art & Sculpture
Working in this manner really makes our juices flow! Art and sculpture account for a significant portion of our work. Corten appears to be very popular right now.


Engineering
To begin with, we don’t do any fabrication in-house. We are not in direct competition with you. We’re a laser-cutting company with a lot of experience; we don’t do design or fabrication. Based on your requirements, we laser cut materials into a variety of shapes.


OEM & Industries
We laser-cut stencils for everything from clean graffiti to wall art. Metal, wood, and miscellaneous stencils are also available for your home, business, or project. From flexible, thin mylar to sturdy metal, we laser cut it all. We can help you choose the best material for your stencil.


Stencils
We’ve cut components for everything from a stencil to intricate decorative panels using laser-cut MDF/Ply. Laser Cutting Processes That Are One-Of-A-Kind Setup requires minimal material waste and no acids or basic adhesives, resulting in better results.


Others
We Have The Technology, Capacity, And Capability To Meet Their Production Needs, Which Is Why We’re So Popular Among Such A Diverse Range Of Customers. They can use us as a one-stop-shop for a variety of materials and processes – and don’t forget, we can laser engrave on almost any material, so if you need a complete laser service, we’re the company to call.
Which Materials Can We Laser Cut
Laser cutting excels at processing a wide range of materials. Laser cutting is commonly used to construct products quickly and easily. We’ve included a list of some of the more common materials below, but if you have a special request, please let us know.


Mild Steel
For us, laser-cut mild steel is the go-to material; we cut more of it than any other. We Take Pride In Buying The Highest Quality Mild Steel Available. Because laser cutting is a quick and precise process, you can expect a good fit and consistent alignment.


Stainless Steel
Stainless steel laser cut is our second most popular material. We offer a wide range of products, including decorative polished panels and components, all with a Nitrogen Clean Cut Edge. All laser cutting is done in our workshop with extreme precision to meet the highest standards.


Aluminum/ Alloy
Laser Cutting Aluminium Has Traditionally Been Difficult Due To Reflections And Thermal Transfer Characteristics. We’ve Invested In Cutting-Edge Technology To Ensure A Clean And Economical Cut. Our equipment is specifically designed to work with aluminum, ensuring a razor-sharp cut and a brilliant finish.


Wood
We’ve created lasers specifically for wood to ensure that the cut quality is excellent and that the material is processed safely. The Edge Is Normally A Darker Color Due To The Thermal Laser Process. The process is a beautifully designed laser cutting machine for cutting wood that takes about 30 seconds to complete from start to finish. It has high processing quality and power, as well as extreme precision.


Plastics
Lasers are excellent at cutting plastics, particularly acrylic. Some plastics, however, are not suitable for laser cutting because the fumes kill our operators! If you have a specific plastic in mind, please let us know. We will be happy to Assist You!


MDF/ Ply
We’ve cut components for everything from a stencil to intricate decorative panels out of laser-cut MDF/Ply. It’s ideal for stairwells, landing surfaces, and decorative paneling in the middle of a room, as it blends in with the wood flooring when placed on the floor.